Do you have a noble idea for a mobile app?
Are you worried that your idea would be used by someone else even before you give it a shape?
Do not lose your sleep worrying. Luckily the intellectual property (IP) law is there to take care of your nightmare. Explicitly speaking, patent, copyright, and trademark laws safeguard your app ideas.
So, how do you patent a mobile app in India? Let us talk about it.
???? Quick Navigation
- Mobile App Definition
- Requirements To Patent Your Mobile App
- Steps for Getting a Patent for Your Mobile App
- How Much Do Patents Cost for a Mobile App
- How Long Does it Take to Patent a Mobile App?
- Mobile App Patenting Alternatives
- How to Get Your Mobile App Patent Approved
- Conclusion
What Is a Mobile App Patent?
A patent is a form of law that restricts your ideas from being used by others without your consent. The law grants you exclusive rights to the idea and what you would want to do with the same.
When you patent your mobile app idea, you do the following:
- Protect your mobile app idea against illegal or unethical use.
- Corroborate the fact that nobody makes a profit by falsely claiming credit for an original idea.
- Considering you are the lawful owner of the idea, it forbids other organizations or people from modifying or selling your idea.
- You have the power to legally accuse any organization, startup, or person of cloning your mobile app idea.
- Seek compensation from any entity that transgresses the patent laws.
Every country has an independent government body that issues patents. For example, in India, it is the Indian Patent Office, also known as the Office of the Controller General of Patents, Designs, and Trade Marks (CGPDTM). This agency is under the Department of Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade. Whereas in the United States, the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) has the authority to issue patents.
Minimum Requirements for Patenting Your Mobile App
One should keep in mind that Saas applications, Software, Mobile applications, or software, “per se” cannot be patented in India as per section 3(k) of the Indian Patents Act. The Indian Patent Office (IPO) classifies any software invention under Computer Related Inventions (CRI) for a patent. However, there is a loophole.
In the case of patenting software, it should be a combination of hardware and software. For mobile applications, the inventor has to decide which part or element(s) of the app needs to be protected from cloning by competitors. Multiple IP rights can cover different aspects of the app. The key is to ensure which part of the app needs patenting and which part requires copyright or trademark.
When you consider a mobile app patent, you should also consider the app’s business longevity. Most apps go out of vogue after six to nine months, and patents are given after 12 months or more. In such scenarios, the cost incurred and time taken are more than the revenue generated by the business.
In the United States, patents are allowed for software-related inventions. The guidelines are not stringent like in India. If you are a startup planning to raise money in the United States, you must have a patent.
Steps for Getting a Patent for Your Mobile App
In India, software patents are given for embedded software in mobile apps or hardware and software combinations only if patent claims are enlisted to secure the innovative aspects of the invention.
The basic steps to follow for patenting a mobile app idea are:

1. Register with a Patent Lawyer
This is the initial step in getting your patent application chosen. You should consult a top-notch patent lawyer who has experience dealing with mobile application patenting. Since it is a legal procedure, it can incorporate litigation. Never try to do it yourself unless you are a patent attorney. Select the best lawyer that fits your budget.
2. Publish Your Mobile App Invention
Just having a mobile app idea isn’t enough for patenting. You need to bring the idea into reality as it is an eligibility criterion to get patented. When the court asks you for evidence of your invention, before deciding on giving a patent, you should have the entire app idea documented with proper flowcharts. Mobile app patent is not given to codes but app procedures and functionalities.
3. Perform a Patent Search
You may have done all necessary checks; however, you should ask your attorney to conduct an online search for mobile app ideas similar to yours or have the same functionalities. This way, you ensure you have the maximum scope of getting your idea patented, and you do not face any breach litigation from other organizations.
4. File a Provisional or a Non-provisional Patent Application
You can file a provisional application or a non-provisional application for your mobile app idea patent application.
If you are filing a provisional application, you can do so without a formal patent declaration, claim, or data disclosure statement. It comes with the following benefits:
- It reviews 12 months for creating the minimum viable product (MVP).
- It is less expensive in comparison to non-provisional applications.
- You can use the term “Patent Pending” on your app.
In a non-provisional application, your patent request should be accompanied by full specifications and claims. You can file for a patent without any app reference mentioned in the procedure.
You should consider a provisional application or a non-provisional application depending on the below factors:
- How quickly you want your patent to be approved.
- Till what time you want to hold the patent text expenses.
5. Submit Your Patent Application
This is the last step in filing for a patent. Please submit the patent application to the concerned office once you have completed the patent application procedure. Applying for a patent is a tedious procedure and requires a lot of paperwork. Some of the essential documents you would need in the process include:
- Application data sheet
- Cover sheet
- Drawings
- Specifications
- Entity status form
- Fee sheet
How Much Do Patents Cost for a Mobile App?
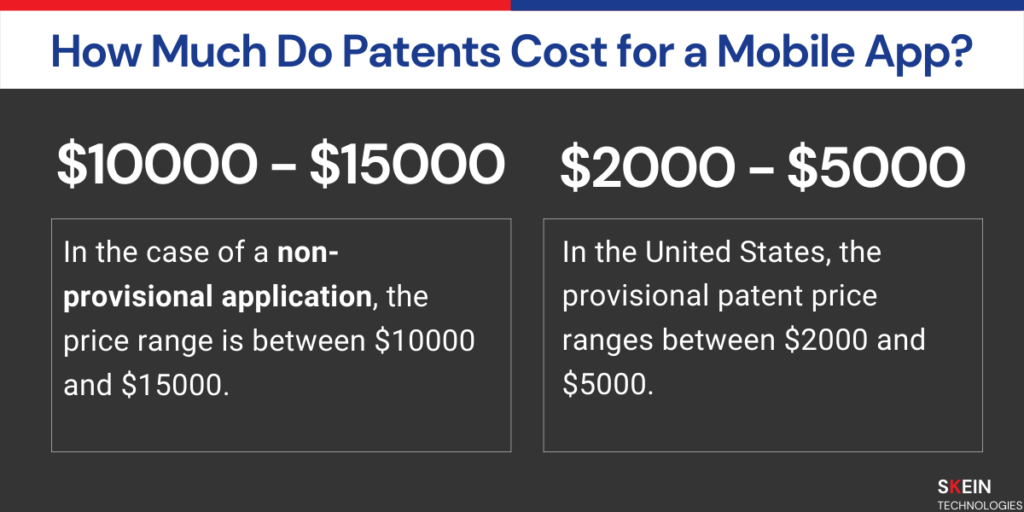
The patent cost for a mobile app varies as per the patent category. In the United States, the provisional patent price ranges between $2000 and $5000. The viability of a provisional patent expires after a year of its acceptance.
In the case of a non-provisional application, the price range is between $10000 and $15000. Hence, an admin entity always holds your patent application for a few years to understand if your idea warrants a patent or not.
In India, the patent fee structure is:
| No | Description | Patent Office Fee (INR) 1$ = ~ INR 75 (E-Filing Only) | Comments | ||
| Other than Natural Person | Natural Person / Startup | ||||
| Small Entity | Other Than Small Entity | ||||
| 1 | Application for grant of patent | 4000 | 8000 | 1600 | Mandatory |
| 2 | Early publication fee | 6250 | 12500 | 2500 | Optional |
| 3 | Request for examination of patent application | 10000 | 20000 | 4000 | Mandatory |
| 4 | For every extra sheet over 30 sheets | 400/sheet | 800/sheet | 160/sheet | Mandatory |
| 5 | For every extra claim over 10 claims | 800/claim | 1600/claim | 320/claim | Mandatory |
The Indian Patent Office charges the least fee for applicants who are natural persons or startups. Applicants other than a natural person are categorized into three types:
- Startup
- A small entity
- Others except for small entities
Please be informed that the fee structure mentioned above is for the e-filing of applications. The Indian Patent Office charges an extra 10% of the total fee for filing done through hard copies.
How Long Does it Take to Patent a Mobile App?
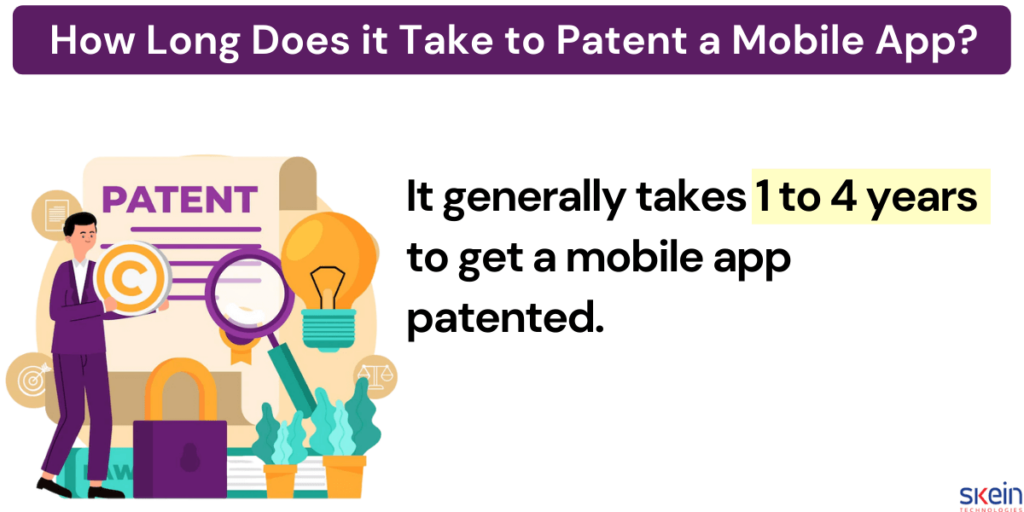
It generally takes 1 to 4 years to get a mobile app patented. The patent application begins with the examination process and is segregated into various factors like specification, abstract, drawings, and claims.
Mobile App Patenting Alternatives and Which One Is Better?

Don’t Hire Us Until You Learn How We Can Help You Develop The Right Application & Grow Your Business.
As mentioned earlier, a mobile app requires several checks before being considered for a patent. An important question crops up in such a scenario: Are there any other methods to safeguard your app idea?
The alternatives to patent are discussed below:
Copyright: With mobile app copyright, you can protect your app code and UI. They are cost-effective, but they only work when someone else replicates your mobile app.
Trademark: Trademark protects the elements that reflect the brand image of your mobile apps, like logos, ads, catalogs, titles, and designs.
Non-disclosure Agreement: Under a non-disclosure agreement (NDA), you prohibit a person from sharing mobile app–related information with others. This mandate is usually for people closely associated with app development, and a violation of the NDA could lead to lawsuits for the person breaching it.
Non-compete Agreement: This agreement prohibits a developer from working with a company that develops similar mobile apps for a fixed period after quitting the current organization.
Patenting is a time-consuming affair. However, the alternatives mentioned above are less time-consuming than mobile app patents. In several cases, it is seen that copyright or trademark is more suitable to protect the app than going for a patent since you cannot patent all parts of the app. Based on which part of the app you need to protect, decide on your protection measures.
How to Get Your Mobile App Patent Approved
Mobile app patenting is a series of processes before a patent is granted. It cannot be just a set of codes but a proper invention that is unique and has not been applied for a patent earlier.
To present your idea at the court, you would have to be prepared with flowcharts, drawings, and prototypes of your mobile app, along with other necessary documentation. At Skein Technologies, we have years of experience developing mobile apps, and we know how to build prototypes. If you have a query related to mobile app development or want to convert an app idea, get in touch with us.
Conclusion
Now that you know how mobile app patenting happens, you will know that it is a challenging activity. However, if you believe that your mobile app idea is strong and an invention, you should go for app patenting. Even though the process is tedious, the end result is sweet.


